Abstract
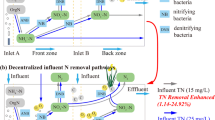
Rural drainage ditches serve as important sinks for heavy metals and antibiotics. However, the combined effects of heavy metals and antibiotics on ecological processes and functions in ditches remain unclear. We studied the combined effects of cadmium and doxycycline on nitrification, denitrification, anaerobic ammonia oxidation, and nitrous oxide emission rates in constructed ditch wetlands during 84 days. Results show that combined pollution decreased denitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation rates, but increased nitrous oxide production rates. The addition of either cadmium or doxycycline decreased the glucokinase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activities, and their combined pollution had a higher impact on adenosine triphosphate than on nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Moreover, the activities of the electron transport system, nitrate reductase, and nitrite reductase were enhanced by short-term pollutant exposure, but inhibited by long-term pollutant exposure. Structural equation modelling further revealed that electron production and transport impacted the rates of denitrification, anaerobic ammonia oxidation, and nitrous oxide production directly and indirectly by changing the activities of nitrate and nitrite reductases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida CMR, Santos F, Ferreira ACF et al (2017) Constructed wetlands for the removal of metals from livestock wastewater—Can the presence of veterinary antibiotics affect removals? Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 137:143–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.11.021
Crini G, Lichtfouse E (2019) Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 17(1):145–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0785-9
Daims H, Lebedeva EV, Pjevac P et al (2015) Complete nitrification by Nitrospira bacteria. Nature 528(7583):504–509. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16461
Dalsgaard T, Thamdrup B, Canfield DE (2005) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) in the marine environment. Res Microbiol 156(4):457–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2005.01.011
Deng Z, Wang Z, Zhang P et al (2019) Effects of divalent copper on microbial community, enzymatic activity and functional genes associated with nitrification and denitrification at tetracycline stress. Enzyme Microb Technol 126:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.03.007
Fan NS, Zhu XL, Wu J et al (2019) Deciphering the microbial and genetic responses of anammox biogranules to the single and joint stress of zinc and tetracycline. Environ Int 132:105097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105097
Han J, Wang C, Deng S et al (2023) China’s sponge cities alleviate urban flooding and water shortage: a review. Environ Chem Lett 232:344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01559-x
He X, Xu Y, Chen J et al (2017) Evolution of corresponding resistance genes in the water of fish tanks with multiple stresses of antibiotics and heavy metals. Water Res 124:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.048
Kartal B, de Almeida NM, Maalcke WJ et al (2013) How to make a living from anaerobic ammonium oxidation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37(3):428–461. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6976.12014
Kartal B, Kuenen JG, van Loosdrecht M (2010) Sewage treatment with anammox. Science 328:702–703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1185941
Li X, Lu Y, Chen Y et al (2021a) Constraining nitrification by intermittent aeration to achieve methane-driven ammonia recovery of the mainstream anaerobic effluent. J Envrion Manag 295:113103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113103
Li ZL, Cheng R, Chen F et al (2021b) Selective stress of antibiotics on microbial denitrification: inhibitory effects, dynamics of microbial community structure and function. J Hazard Mater 405:124366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124366
Liao Q, Li M, Dong Y et al (2019) Impacts of Cu and sulfadiazine on soil potential nitrification and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environ Pollut Bioavailab 31(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/26395940.2018.1564629
Ma L, Li Z, Liu G et al (2023) Low-level cadmium alleviates the disturbance of doxycycline on nitrogen removal and N2O emissions in ditch wetlands by altering microbial community and enzymatic activity. J Clean Prod 387:135807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135807
Martins VV, Zanetti MOB, Pitondo-Silva A et al (2014) Aquatic environments polluted with antibiotics and heavy metals: a human health hazard. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(9):5873–5878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2509-4
Su X, Chen Y, Wang Y et al (2019) Impacts of chlorothalonil on denitrification and N2O emission in riparian sediments: Microbial metabolism mechanism. Water Res 148:188–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.10.052
Wang K, Wu Y, Li W et al (2018) Insight into effects of mature compost recycling on N2O emission and denitrification genes in sludge composting. Bioresour Technol 251:320–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.12.077
Wehrfritz JM, Reilly A, Spiro S et al (1993) Purification of hydroxylamine oxidase from Thiosphaera pantotropha: identification of electron acceptors that couple heterotrophic nitrification to aerobic denitrification. FEBS Lett 335(2):246–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(93)80739-H
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (32371714 and 32022051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LM helped in experimental method development, data collection and analysis, and manuscript writing. ZL helped in experimental work. GH helped in experimental work. GL worked in project supervision. MJ helped in data analysis. WL helped in funding acquisition, project supervision, and manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, L., Li, Z., He, G. et al. Effect of combined cadmium and doxycycline pollution on the nitrogen cycle in constructed ditch wetlands. Environ Chem Lett 22, 989–995 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-024-01697-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-024-01697-4